Chemical intermediate is any chemical substance produced during the conversion of some reactant to a product. Most synthetic processes involve transformation of some readily available and often inexpensive substance to some desired product through a succession of steps. All the substances generated by one step and used for the succeeding step are considered intermediates. A reaction intermediate or an intermediate is a molecular entity that is formed from the reactants (or preceding intermediates) and reacts further to give the directly observed products of a chemical reaction. Pharmaceutical Formulation Intermediates (or PFI) is a commercial terminology used for Direct Compressible (DC). It comprises a mixture of active substances and excipients, usually in powder form.
-
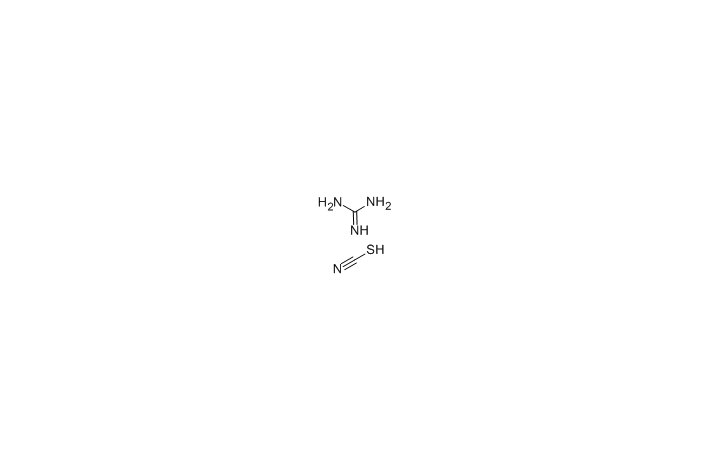
Cas.NO:593-84-0
Guanidine thiocyanate -
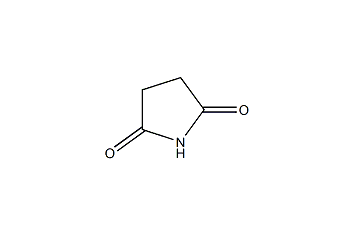
Cas.NO:123-56-8
Succinimide -
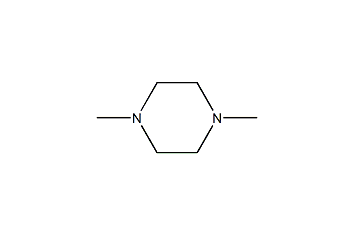
Cas.NO:106-58-1
N,N-Dimethylpiperazine -
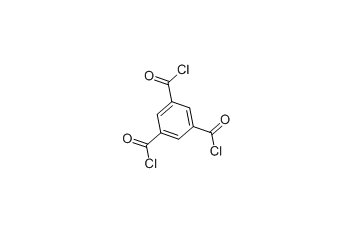
Cas.NO:4422-95-1
1,3,5-Benzenetricarboxylic acid chloride -
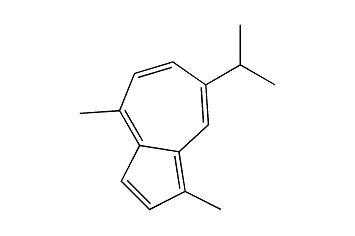
Cas.NO:489-84-9
Guaiazulene -
Cas.NO:563-96-2
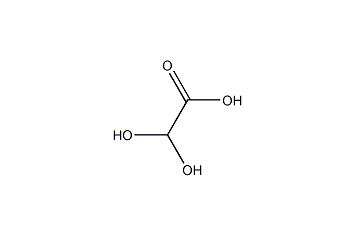
Glyoxylic acid monohydrate -
Cas.NO:123-93-3
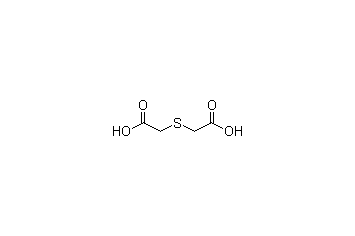
Thiodiglycolic acid -
Cas.NO:1008-72-6
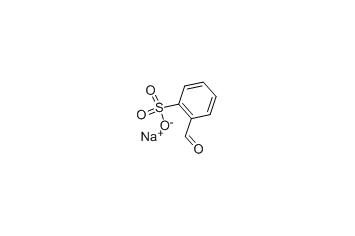
2-Formylbenzenesulfonic acid sodium salt -
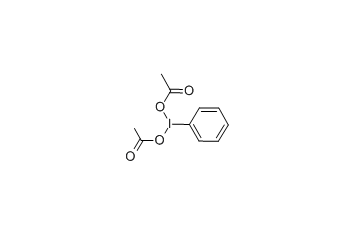
Cas.NO:3240-34-4
Iodobenzene diacetate -
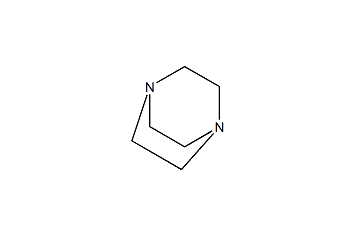
Cas.NO:280-57-9
Triethylenediamine -
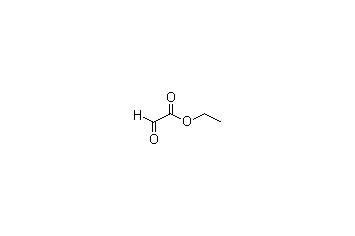
Cas.NO:924-44-7
Ethyl glyoxalate -
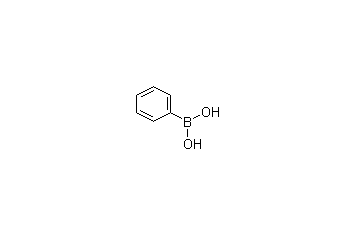
Cas.NO:98-80-6
Phenylboronic acid

